Accu•SAL™
Oral Fluid Collection System
The collection of alternative specimens such as urine, hair, sweat, tears, saliva and others is growing in importance as an alternative to blood sampling. A number of kits exist that allow for the collection of various forms of oral fluid or saliva and each has specific application in the growing market for salivary testing.
Despite the availability of a number of oral fluid collection kits, there are few offering standardized collection of oral fluids for drug and drug metabolite testing with a means of confirmation of sample sufficiency. Accu•SAL™ incorporates a novel Sample Volume Adequacy Indicator built into the device handle and provides a suitable quantity of oral fluids and whole saliva for a variety of drug testing applications. A unique feature of the Accu•SAL™ Kit is that in the case of a “short sample”, the user is able to calculate the absolute quantity of saliva collected, and from that, an accurate dilution factor for the downstream immunoassay.
Principles of the Kit
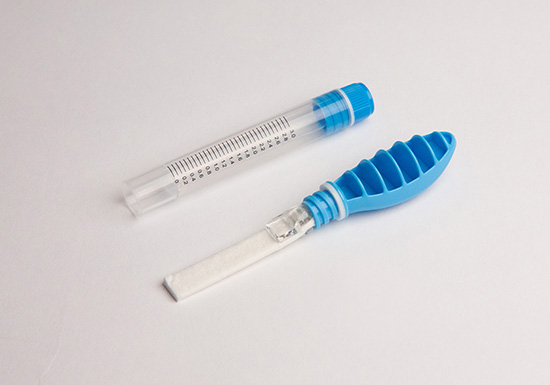
The Accu•SAL™ Oral Fluid Collection System is a proprietary patented kit for the standardized collection of whole saliva from the pool of saliva that collects in the mouth. In order to collect an adequate specimen, it is recommended that patients/subjects “pool” saliva in the mouth just prior to sample collection to facilitate faster collection times. The Accu•SAL™ Oral Fluid Collection System features a collection strip comprised of an absorbent pad material, which is placed into the pool of saliva that collects in the mouth to collect the sample. After 1-2 minutes, a Sample Volume Adequacy Indicator (SVAI) changes from yellow to blue signifying sufficient saliva has been collected for subsequent analysis. The Collection Strip is then transferred to a transport tube for delivery to a laboratory. Upon receipt at the laboratory the sample is removed by vortexing or centrifugation and is then ready for drug or alternate analysis by various methods.
Documentation
Accu•SAL™ Step by Step Instructions
Publications
Human Saliva: A Future Diagnostic Tool (Kurshid, Z. 2016)
